3. 课后练习-图像处理
本文最后更新于 2025年6月4日 晚上
课后练习2
Required libs:Numpy PIL Scipy Matplotlib cv2
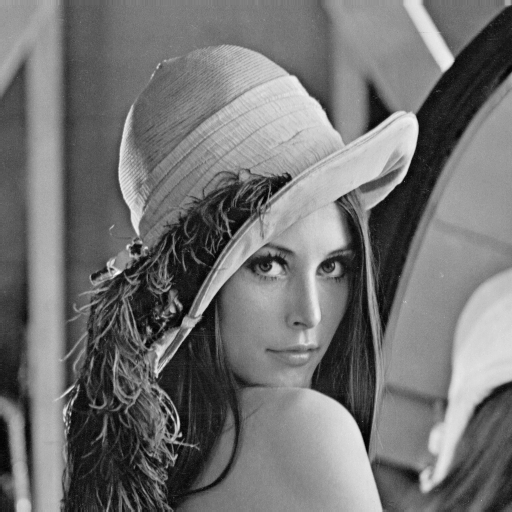
Q1. Write a python script to open the “lena.png” file using opencv.
- Display the opened image in a new window named “Display Lena”
- Save the image to a new file named “lena_resaved.png”

1
2
3
4
5import cv2 as cv
img = cv.imread("lena.png") # cv2.imread('path') read the img
cv.imshow("Display Lena",img) #cv2.imshow(windowname,path)
cv.waitKey(0) #to let the window display until clicking/pressing
cv.imwrite("lena_resaved.png",img) #cv2.imwrite(filename,path,params)
Q2. Use PIL and Matplotlib libraries for Q2.
Use “lena.png” to perform following operations and save the images:
- Crop a section from the image whose vertices are (100,100), (100,400), (400,100), (400,400).
(hint: convert the cv2 image into PIL Image)
- Rotate the cropped image by 45 degrees counter-clockwise.
- Perform histogram equalization on lena.png. (hint: use ImageOps.equalize from PIL)
- Use matplotlib to plot the histogram figure for both original image and processed image.
(hint: use histogram() function in PIL)
- Perform Max Filtering, Min Filtering, and Median Filter on lena.png. (hint: PIL.ImageFilter)
- Perform Gaussian Blur with sigma equal to 3 and 5. (hint: PIL.ImageFilter)

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43import cv2
from PIL import Image
from PIL import ImageOps
from PIL import ImageFilter as filter
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
pil_img=Image.open("lena.png") #open img in pil
#(in cv2 lib, img is opened as array)
# load cv img: Image.fromarray()
pil_img.show() # show the img
img_crop = pil_img.crop((100,100,300,300)) #crop((start point,hight,width))
img_crop.show() #show the img
img_rota = img_crop.rotate(45) #rotate(degree)
img_rota.show()
img_eql=ImageOps.equalize(pil_img)
#ImageOps.equalize(path) histogram equalize the imge
plt.plot(range(0,256),img_eql.histogram())
#pyplot(aix,img) plot someting
#img.histogram() return the histogram
plt.show()
plt.show(rang(0,256),pil_img.histogram())
plt.show()
img_max = pil_img.filter(filter.maxfilter())
#filter.(Imagefilter.parm()) add filters
img_max.show()
img_min=pil_img.filter(filter.minfilter())
img_min.show()
img_mid=pil_img.filter(filter.medianfilter())
img_mid.show()
img_gus3=pil_img.filter(filter.gaussianblur(radius=3))
img_gus3.show()
img_gus10=pil_img.filter(filter.gaussianblur(radius=10))
img_gus10.show()
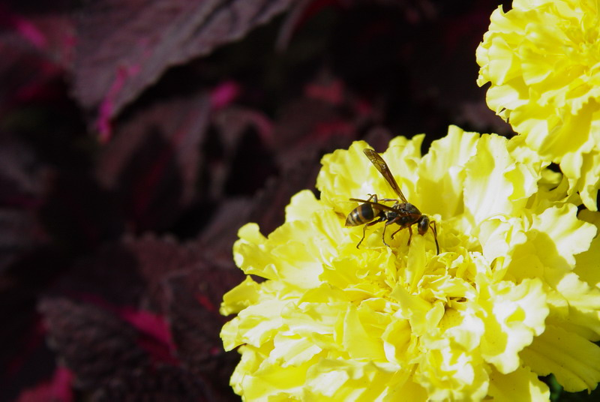
Q3. Colour space conversion. Use Python OpenCV functions to perform following operations on
“bee.png” and save the images at each step.
- Read the image.
- Convert the image to HSV(Hu Satuation Value:包含了三个通道:单色(H),饱和度(S),灰度(V)) color space.
- Perform histogram equalization on V channel by cv2.equalizeHist().
- Convert the result image to BGR color space.
- Show the image by cv2.imshow() and save the image.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16import cv2
from PIL import ImageOps
from PIL import ImageFilter as filter
bee_img = cv2.imread("bee.png")
bee_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(bee_img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
bee_hsv.imshow()
bee_hsv[:,:,2]= cv2.equalizeHist(bee_hsv[:,:,2])
# 2 presents the channel 2: V
bee_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(bee_hsv,cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
cv2.imshow("norm",bee_rgb)
bee_img[:,:,2]= cv2.equalizeHist(bee_rgb[:,:,2])
bee_img = cv2.cvtColor(bee_hsv,cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
cv2.imshow("rgb",bee_img)
3. 课后练习-图像处理
https://l61012345.top/2021/01/26/Machine Learning-NAU/3.a 课后练习/